Designing Tomorrow: Build Your Vision with a Degree in Pharmacy
• Aptitude
• Interview preparation
• Mentorship from Industry Mentors
• Group Discussion
Students can opt for Internships after 1st year of the Program
Placements Interviews
Guaranteed
• Certified Geriatric Pharmacist
• Clinical Data Management
• Regulatory Affairs Certification
• Compounding Pharmacy Certification
• Group Discussions
• Workshops and Seminars
• Urban Sites
• Rural Sites
• Heritage Sites
• Modern Sites
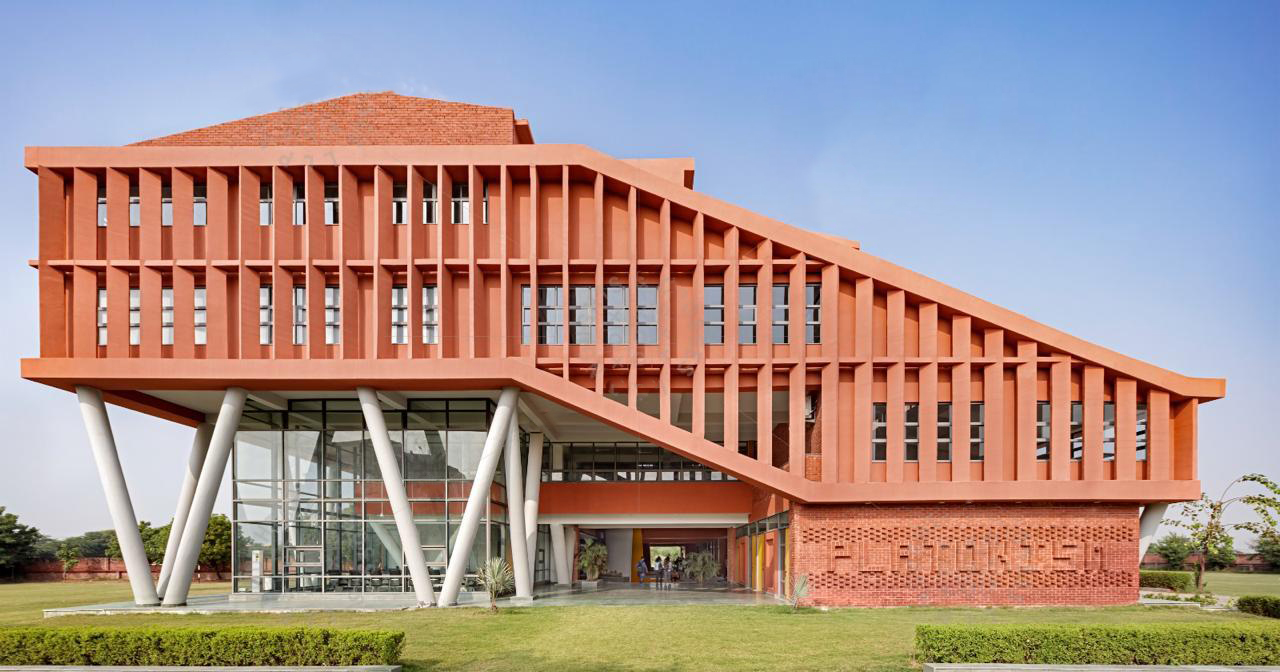

St. Andrews college of Pharmacy (SACP) is situated in the industrial hub of India, Gurgaon, part of the Delhi National Capital Region (NCR). Known for its strategic location, the institute offers students the advantage of being in proximity to numerous multinational corporations and industrial enterprises. This provides ample opportunities for internships, industry interactions, and practical exposure, enhancing the overall learning experience. SACP is committed to delivering high-quality education in Pharmacy, combining rigorous academic curriculum with real-world applications. The institute boasts state-of-the-art infrastructure, experienced faculty, and a vibrant campus life, fostering a conducive environment for holistic development and professional growth.
By achieving these course objectives, the B.Pharm program aims to prepare students to become competent, ethical, and innovative pharmacists who can contribute effectively to the healthcare system and advance the field of pharmacy. Here are some typical objectives of a pharmacy (B. Pharm) course:
Comprehensive Understanding of Pharmaceutical Sciences:
Practical and Laboratory Skills:
Healthcare Systems and Public Health:
Pharmacy Practice and Patient Care:
The Bachelor of Pharmacy (B.Pharm) program typically spans four years, divided into eight semesters. The course structure is designed to cover a wide range of subjects, from basic sciences to specialized pharmaceutical topics, along with practical training and research projects..
This is usually a four-year undergraduate program divided into eight semesters.
B Pharma course curriculum includes subjects such as pharmacology, medicinal chemistry, pharmaceutics, pharmacognosy, and pharmacy practice. In the B Pharma course, students learn about drug formulation, therapeutic drug monitoring, and the regulatory aspects of the pharmaceutical industry…
By following this structured course outline, the B.Pharm program aims to produce well-rounded, competent pharmacists ready to meet the demands of the healthcare industry and contribute to the advancement of pharmaceutical sciences.
1: Foundation and Basic Sciences
2: Core Pharmaceutical Sciences
3: Advanced Pharmaceutical Sciences
4: Specialized Topics and Research
The B.Pharm program uses a combination of continuous assessment (assignments, quizzes, practical exams) and end-of-semester examinations to evaluate students’ understanding and performance. Additionally, project work and internships are assessed based on reports, presentations, and supervisor evaluations.
Developing content for B.Pharm (Bachelor of Pharmacy) students typically involves providing educational and practical information relevant to their coursework, career aspirations, and professional development.
Creating assessments and activities in pharmacy is crucial for reinforcing learning, evaluating understanding, and enhancing practical skills.
Assessments
Activities
Creating a comprehensive plan for support and resources in a Bachelor of Pharmacy (B. Pharma) program involves addressing various academic, professional, and personal needs of students.
Academic Support
Professional Development
Personal Support
Technological Resources
Community and Extracurricular Activities
Curriculum Outline for B. Pharma and D. Pharma-
Programme Subjects

“Pharmacy is a field where compassion meets precision. Embrace both, and you will not only succeed academically but also make a meaningful impact on the lives of your patients.”

“Your journey in pharmacy is about more than just medications. It’s about understanding people, building trust, and providing the best care possible. Strive to be the pharmacist patients can rely on.”

“Pharmacy is an evolving field. Stay informed about the latest developments, adapt to new technologies, and always be prepared to contribute to the progress of our profession.”

“Precision in pharmacy practice is crucial. Pay attention to detail, understand the kinetics of each drug, and ensure that your dosing recommendations are spot-on for optimal patient outcomes.”
The placement season has been exceptionally successful this year, reflecting the high caliber of our students and the strong industry connections we have cultivated.





Recruiters for Placements
Highest package offered
Average CTC
100% ROI on Tuition Fee
Review opportunities.
Infrastructure – Providing excellent infrastructure facilities is crucial for a pharmacy college to ensure comprehensive education, practical training, and overall development of its students. Below are the key infrastructure facilities that should be available for pharmacy students:
Use our Virtual Tour to explore St. Andrews college of Pharmacy (SACP) is located in the industrial hub of India Gurgaon, Delhi (NCR) at your convenience. See yourself in our classrooms, laboratories, residence halls, and more. The Campus Virtual Tour is always available and never reaches capacity.
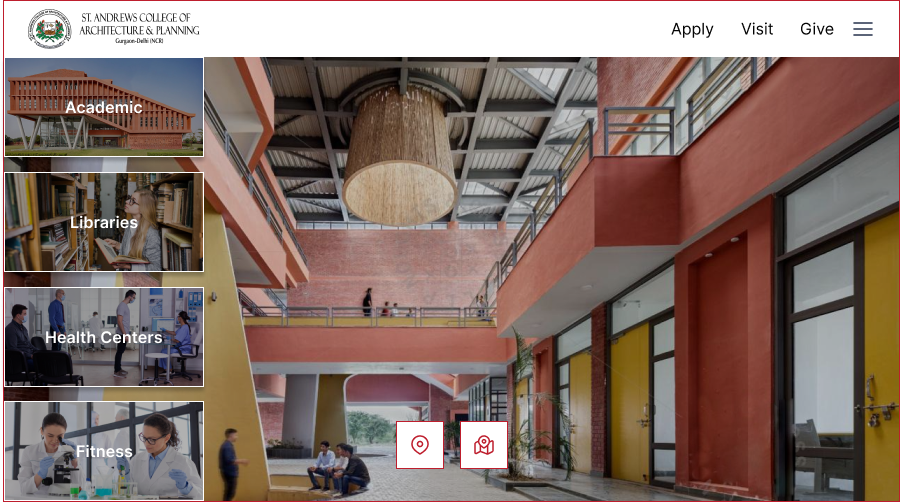
St. Andrews College of Pharmacy Farrukhnagar, Gurugram- 122506
+91-8505937772
admissions@saitm.org
Registering for orientation in a pharmacy program typically involves a few steps.
Steps to Register for Pharmacy Orientation
Tips for a Smooth Registration Process
Financial support for pharmacy students can come in various forms, depending on the institution and the country.
Types of Financial Support
Obtaining an education loan to finance your pharmacy studies involves several steps.
Scholarships for pharmacy students come in various types, often based on merit, financial need, background, or specific interests within the field of pharmacy.
St. Andrews college of Pharmacy may charge lower fees compared to other private institutions for several reasons
Factors Influencing Lower Fees
The fee structure for B. Pharma (Bachelor of Pharmacy) program is Rs 98500/- per year
Bachelor of Pharmacy programs offer promising job prospects in various sectors of the pharmaceutical industry.
Job Prospects for B. Pharma Graduates:
The choice between a B. Pharma (Bachelor of Pharmacy) and D. Pharma (Diploma in Pharmacy) depends largely on your career goals, educational background, and the specific requirements of the pharmaceutical industry in your region.
(Bachelor of Pharmacy)
(Diploma in Pharmacy)